What Is a DNS Server and Why Is It Unavailable?
A DNS server, short for Domain Name System server, is a computer that translates domain names into IP addresses. Without DNS, accessing any website using its domain name would not be possible. DNS servers play a critical role in the functioning of the internet, and any issues with them can lead to connectivity problems for users.
When a user types in a web address, the DNS server looks up the IP address associated with that name and directs the user to the appropriate server where the website resides. This translation is necessary since humans prefer to use domain names while computers prefer numerical IP addresses.
However, at times, DNS servers can become unavailable, leading to issues with internet connectivity. Some common reasons why DNS servers may become unavailable are:
1. Overload: Like any other server, a DNS server can get overloaded due to too many requests. An overload can lead to slowed response times or even complete unavailability.
2. Configuration changes: If configuration changes or upgrades are made to DNS servers, they may be unavailable for a brief period.
3. Network outages: Network failures can make the connection to the DNS server unavailable, leading to an inability to translate domain names into IP addresses.
4. Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks: DDoS attacks can overload the DNS server with an excess number of requests, rendering it unavailable.
When a DNS server becomes unavailable, it may appear that the user is disconnected from the internet because the DNS server cannot resolve domain names. The user may receive error messages such as “DNS Server Not Responding,” “DNS Lookup Failed,” or “This Site Can’t Be Reached.”
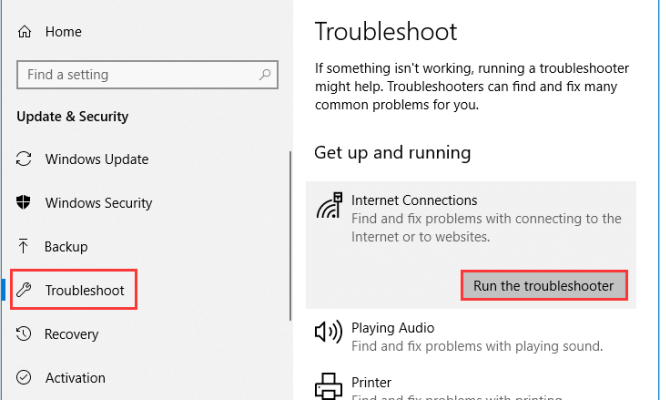
To resolve any DNS server issues, one can try the following methods:
1. Rebooting the DNS server: A restart of the DNS server can help in some cases to resolve the issue.
2. Changing the DNS server: Switching to a different DNS server can sometimes fix connectivity issues.
3. Contacting the ISP or IT department: Contacting the internet service provider or IT department can help identify any specific issues with the DNS server and resolve the problem faster.