What You Need to Know About Color Separations in Printing
Printing is an essential part of any business, whether it’s for marketing collateral, product packaging, or any other type of print material. Color separation is a crucial element of the printing process that requires careful consideration to ensure quality prints.
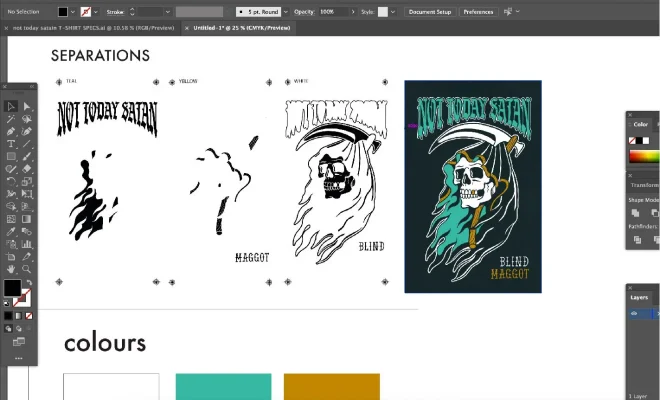
Color separation is the process of breaking down an image into its basic color components, which are then printed individually. Images are typically composed of RGB (red, green, blue) colors, but printing techniques use different color models such as CMYK (cyan, magenta, yellow, and black) or Pantone Matching System (PMS) to produce desired colors.
CMYK printing model is commonly used in offset printing, digital printing, and direct-to-garment printing, while the PMS system is used for specific spot colors. Understanding these color models is essential when creating artwork for printing.
To ensure accurate color prints, it is essential to have an understanding of how to separate colors. There are two main types of color separations: process color and spot color.
Process color separation is used in CMYK printing and involves separating images into four primary colors: cyan, magenta, yellow, and black. This process is used to create a broad range of colors in various shades and hues. The resulting printed product has a softer, slightly blurred look due to the splitting of colors.
Spot color separation, on the other hand, involves printing with specific colors beyond the use of standard process colors. The PMS system uses pre-mixed inks to achieve these distinct colors. Spot colors tend to appear sharper and brighter than those produced by process color separation.
When designing artwork for print, it is essential to take into account the type of color separation required. Always use high-quality images with high-resolution to avoid blurry images. It’s also best to use Pantone’s solid-coated color guide when using spot colors, as it provides a better visual representation of how your colors will appear in print.
Color separation also affects the cost of printing. A design with spot colors is typically more expensive than artwork that uses process color separation. Process printing enables using multiple colors to create different shades in a single image.
In conclusion, effective color separation is a vital part of the printing process. Understanding the types of color separations, color models, and design guidelines for each type can make a significant difference in print quality, especially when working with complicated artwork. By implementing these best practices, you can ensure high-quality prints that represent your brand’s image and leave a lasting impression on your audience.