What is Non-Volatile Memory (NVM)?
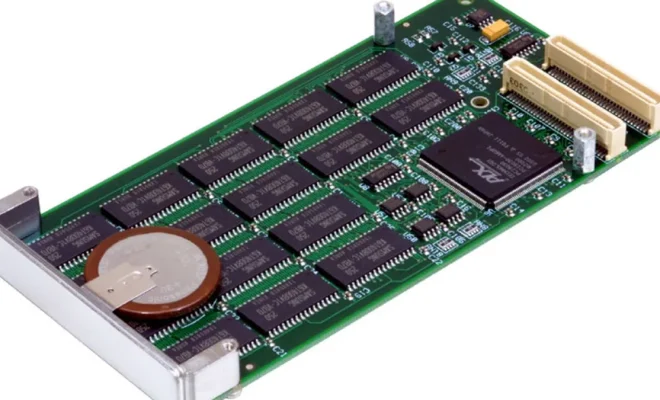

Non-volatile memory, or NVM, is a type of computer memory that retains its contents even when the power is turned off. Unlike volatile memory, such as random access memory (RAM), which needs a constant source of power to hold data, NVM retains data even when the power is removed. This makes it ideal for storing critical data that needs to be accessed quickly, such as boot files, system settings, and other essential information.
There are several types of non-volatile memory technologies available, including flash memory, read-only memory (ROM), and Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory (EEPROM). Flash memory is commonly used in consumer electronics devices, such as USB flash drives and SD cards, while ROM is typically used to store firmware in embedded systems. EEPROM is used in applications where data needs to be stored but modified frequently, such as in computer BIOS settings.
One of the primary advantages of NVM is its durability and reliability. Since it does not rely on a constant source of power to hold data, it is not affected by power outages or other interruptions. This makes it ideal for use in applications that require high levels of reliability, including aviation, automotive, and medical devices.
Another benefit of NVM is its speed. Since it is physically accessed through electronic circuits rather than mechanical parts, NVM can be accessed much faster than traditional hard disk drives or other types of storage media. This makes it ideal for use in applications that require fast access to data, such as in financial trading or scientific research.
Despite its many advantages, there are some limitations to NVM. For example, it typically has a limited number of write cycles before it begins to degrade, which can impact its overall lifespan. Additionally, some types of NVM, such as EEPROM, can be relatively expensive compared to other types of memory.
In conclusion, non-volatile memory is an essential component of modern computing systems. It provides a reliable, fast, and efficient way to store and access data, making it ideal for use in a wide range of applications. As technology continues to evolve, new types of NVM are likely to emerge, enabling even more advanced and sophisticated computing systems in the future.