What Is CMOS and What Is It For?
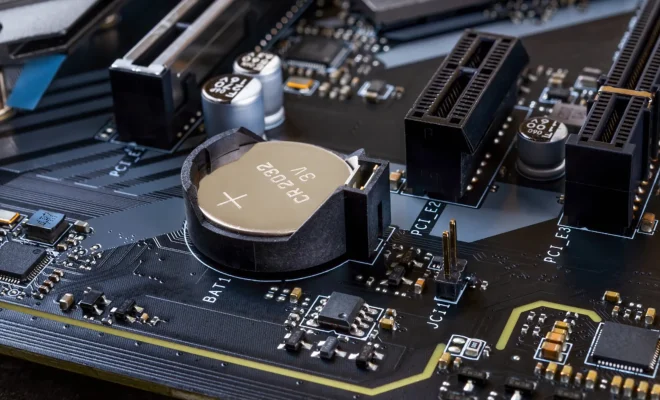
Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor or CMOS is a type of semiconductor technology used in electronic devices. It is widely used in computer circuitry and digital cameras, as well as in radios, televisions, and even alarm clocks.
The primary function of CMOS is to store and process digital data in a low power, low voltage environment. It is a versatile technology that has been used in electronic devices for many years, with its importance only growing as technology continues to advance.
One important feature of CMOS is its ability to maintain data even when the device is turned off. This makes it a reliable, non-volatile storage solution for all kinds of data, ranging from BIOS settings to photos.
The low power consumption of CMOS means it is also an ideal choice for digital devices that rely on battery power. This is because it uses very little electricity, allowing the device to run for a longer period without needing to recharge.
In computer circuitry, CMOS technology is used to create CPU chips that act as the brains of the computer. These chips use CMOS technology to process and store data, which is then sent to other components and peripherals.
Another important use of CMOS is in cameras. In digital cameras, CMOS sensors capture images in a sensor array, which is then converted into a digital signal before being stored on a memory card. This technology allows for high-resolution images to be captured quickly, making it an excellent choice for professional photographers and hobbyists alike.
In conclusion, CMOS technology is a critical component in modern-day electronics. Its low power consumption, volatility, and ability to store data make it an ideal choice for a variety of devices. Its versatility makes it a popular choice, ensuring its continued relevance in the world of electronics.