Memory Sizes Explained: Gigabytes, Terabytes, and Petabytes in Context
Memory sizes have become a vital aspect of our daily lives. We rely on memory sizes to store and access vital information, such as music, movies, documents, and photos. But when it comes to memory sizes, it is essential to understand the context behind the different units used to define the memory’s capacity. In this article, we will explain gigabytes, terabytes, and petabytes in context to help you understand what each memory unit means.
Gigabyte (GB)
The gigabyte is the most common measurement unit concerning memory size. It describes the amount of storage space available in a device or system. A gigabyte is equivalent to 1,000 megabytes, and it can hold a considerable amount of information. For example, a single gigabyte can store about 200 songs or over 500 photos.
The Gigabyte is essential when it comes to consumer technologies such as computers, smartphones, and tablets. It is crucial for storing documents, music, videos, and photos.
Terabyte (TB)
Terabyte is a larger unit of measurement concerning memory size. A terabyte is equivalent to 1,000 gigabytes, which is a considerable amount of storage. It is usually required in specialized industries that require more extensive storage, such as video production and online gaming.
Terabyte-sized memory is also essential for consumers who need to store massive files, such as high-quality videos, photos, and high-resolution games. Additionally, terabytes are also important for those who have multiple devices to store data on – such as a home media server – that require more extensive storage than consumer devices.
Petabyte (PB)
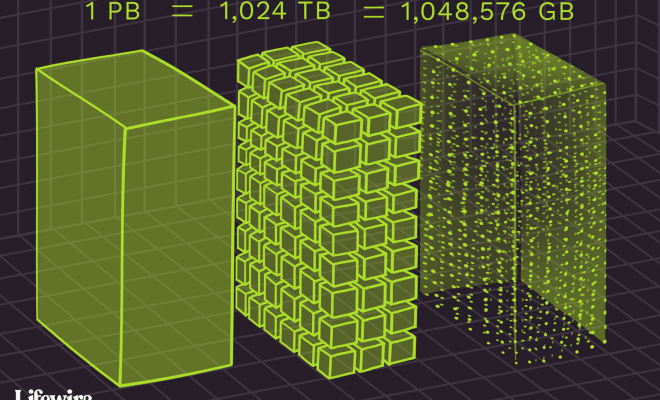
The petabyte is the largest memory size unit. It is equivalent to 1,000 terabytes, which equals around 1,000,000 gigabytes. Petabytes of data are required in specialized industries such as scientific research, healthcare, and national security.
For example, NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope collects 10 to 20 terabytes of data each year. Simultaneously, large data centers like Microsoft and Google store petabytes of data to provide cloud services to their customers.
Wrapping up
Understanding memory sizes is crucial to help us pick the right device or system for our needs. The gigabyte is perfect for consumer technologies that require standard storage. Meanwhile, terabyte-sized memories are required for larger homes or niche industries that require vast storage space for sizable file storage.