Mean Opinion Score (MOS): A Measure of Voice Quality
Mean Opinion Score (MOS) is a commonly used standardized method of measuring voice quality in telecommunication networks. It is used to assess and evaluate the quality of voice calls as perceived by human listeners.
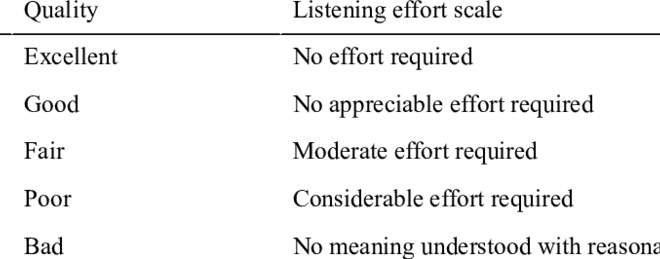
MOS is a subjective method, relying on human perception of voice quality. Typically, a sample of listeners is presented with a set of voice recordings, which are played back through a communication network. Listeners are then asked to rate the quality of each recording on a scale ranging from poor to excellent. The MOS is then calculated as an average of all the ratings, giving a single score that reflects the overall quality of the voice transmission.
MOS scores are typically reported on a scale of 1 to 5, with 1 being the lowest score and 5 being the highest. A score of 1 indicates that the voice quality is so poor that the communication is essentially unusable. A score of 5 indicates that the voice quality is excellent, and listeners can easily understand and follow the conversation.
MOS is used in a variety of applications, including voice over IP (VoIP) systems, cellular networks, and traditional landline telecommunication networks. In each of these situations, the MOS is used to evaluate the quality of voice transmissions and to identify potential problems or areas for improvement.
One of the benefits of using MOS is that it is a standardized method that can be used across different networks and technologies. This makes it easy to compare the quality of different voice communication systems and to identify best practices for ensuring good voice quality. Additionally, because MOS is based on human perception, it provides a measure of voice quality that is meaningful to end-users, who are ultimately the ones who benefit from good voice quality.
To ensure good voice quality and high MOS scores, it is critical to use high-quality networking equipment, including routers, switches and IP phones. Additionally, network administrators should monitor the network for issues such as packet loss, network congestion, and other factors that can degrade voice quality. By taking these steps, businesses and organizations can ensure that their voice communication systems provide high-quality voice transmissions that are easy to understand and follow.
In conclusion, MOS is a valuable tool for evaluating voice quality in telecommunication networks. By relying on human perception, MOS provides a measure of voice quality that is meaningful to end-users, helping to ensure that voice communication systems meet the needs and expectations of the people who rely on them. As businesses and organizations continue to rely on voice communication for critical functions, MOS will remain an important tool for ensuring that those communication systems provide high-quality, reliable voice transmissions that meet the needs of end-users.