How Do Bits, Bytes, Megabytes, Megabits, and Gigabits Differ?
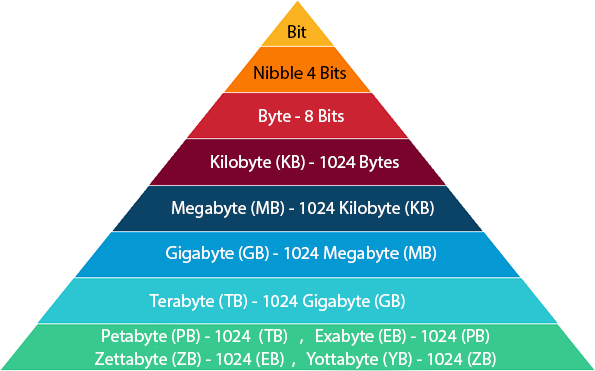
In the world of computing, terminologies such as bits, bytes, megabytes, megabits, and gigabits are commonly used for measuring data, storage capacity, and speed. They are all related to each other, with each unit representing a different value or measurement. Understanding the differences between these units is essential for anyone working with computers, networks, or storage systems.
Bits are the smallest and most basic unit of measurement for digital data. A bit is a binary digit that can only be one of two values, 0 or 1. It is the building block of all digital communications and computing, and it represents the smallest piece of data that a computer can handle.
In contrast, bytes are a larger unit of measurement that consists of eight bits. This means that a byte can represent 256 different values (2^8), ranging from 0 to 255. Bytes are commonly used for measuring file sizes, storage capacity, and memory. For example, a typical song in MP3 format might be around 3-4 megabytes (MB), or approximately 30 million bytes (3-4 x 10^6).
Meanwhile, megabytes and megabits are both used for measuring digital data, but they represent different values. Megabytes (MB) are used to measure file sizes, storage capacity, and memory. One megabyte is equal to 1,000,000 bytes, or approximately one million characters of text. Megabits (Mb), on the other hand, are used to measure data transfer rates and network speeds. One megabit is equal to 1,000,000 bits, or approximately 125,000 bytes.
Finally, gigabits (Gb) are used to measure data transfer rates and network speeds. One gigabit is equal to 1,000,000,000 bits, or approximately 125,000,000 bytes. Gigabits are commonly used for measuring internet speeds, as well as for storage devices such as hard drives and solid-state drives.
In conclusion, bits, bytes, megabytes, megabits, and gigabits are all important units of measurement in the world of computing. Each unit represents a different value or measurement, and understanding their differences is crucial for anyone working with digital data, storage, or communication systems. Whether you are measuring file sizes, network speeds, or storage capacity, knowing the right units to use is essential for accurate and efficient data management.






