Home networking: Everything you need to know
Introduction
In today’s technology-driven world, having a reliable home network is essential. From streaming movies to browsing the internet and even working from home, a robust network ensures uninterrupted access to all your online activities. However, setting up and maintaining a home network can be quite a challenge for many. In this article, we’ll delve deep into everything you need to know about home networking.
1. Identify Your Networking Needs
Before diving into the world of home networking, it’s crucial to determine your needs. Think about how many devices will connect to your network and the type of online activities you engage in daily. Remember, your network should support bandwidth-hungry applications like gaming and streaming without any hiccups. Your networking needs will determine the type of equipment you’ll require.
2. Choosing the Right Networking Equipment
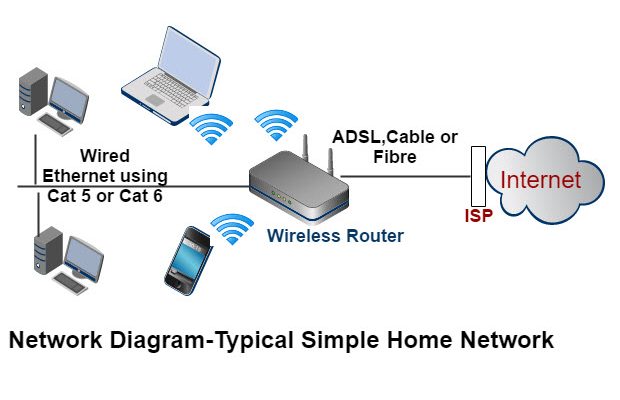
Setting up a home network requires essential components such as a modem, router, switches or hubs, and cabling or wireless access points. Choosing the right equipment depends on factors such as your internet service provider (ISP), connection speeds, wired vs. wireless connections, and overall network size.
a) Modem: A modem connects your home network to the internet through your ISP. Ensure that it supports the maximum speed offered by your ISP for optimal performance.
b) Router: A router acts as the hub of your network, directing traffic between devices and the internet. Depending on your budget and requirements, you can opt for a standard router or an advanced router offering features such as Quality of Service (QoS) and parental controls.
c) Switches/Hubs: Switches are responsible for forwarding data to connected devices based on their unique addresses. Hubs act similarly but send data indiscriminately to all connected devices.
d) Wireless Access Points: For wireless connectivity throughout your home, consider investing in wireless access points or mesh networking systems.
3. Wired vs. Wireless Networking
a) Wired Networking: More reliable and faster, wired connections are ideal for data-heavy tasks and proximity to the router. Ethernet cables (Cat 5e, Cat 6, or Cat 7) provide varying data transfer speeds and suit different networking requirements.
b) Wireless Networking: The most popular form of connectivity, wireless networks offer freedom of movement but can be subject to interference from appliances, walls, and other electronic devices. Wi-Fi routers support different standards like 802.11ac (Wi-Fi 5) or the more recent 802.11ax (Wi-Fi 6) – each with varying speeds and features.
4. Network Setup and Configuration
Once you have the right equipment, it’s time to set up your network. Connect your modem to the router via an Ethernet cable if not integrated, then configure your router with a unique network name (SSID), strong password, and security measures such as WPA2 or WPA3 encryption.
5. Extend Your Network Range
Larger homes or those with obstacles may require repeaters, extenders, or mesh systems to ensure consistent Wi-Fi signals throughout the property.
6. Regular Maintenance
Keep your network running smoothly by updating firmware periodically, resetting devices as needed, and repositioning routers or access points for optimal signal distribution.
Conclusion
Setting up a home network need not be intimidating! By considering your networking needs and opting for the right equipment, you can enjoy seamless connectivity across all your devices. Keep in mind that regular maintenance plays a crucial role in ensuring a consistently reliable network experience.