Wireless Local Area Networking Explained
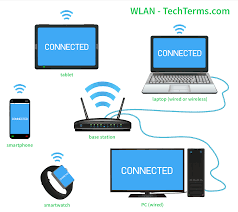
Wireless Local Area Networking, also known as WLAN or Wi-Fi, is a modern technology that provides wireless access to the internet or other network resources within a specific area. In a traditional Local Area Network (LAN), a wired connection is used to establish connectivity among devices within a geographical location. However, with the rise of modern communication technologies, WLAN has emerged as a viable alternative to traditional LAN setups.
Wireless Local Area Networking uses radio waves to transmit data over short distances. These radio waves are typically in the range of 2.4GHz or 5GHz and can carry data at high speeds over the air. WLAN uses a wireless access point (WAP) to route traffic between devices and to connect the WLAN to the wider internet.
A WLAN setup typically consists of a few essential components. These are the wireless access point (WAP), network interface controllers, and devices that connect to the network. The WAP is the central hub that routes traffic between devices and connects the WLAN to the wider internet. Network interface controllers, such as wireless network cards or routers with built-in wireless capabilities, are used to connect devices to the WLAN. Finally, devices such as laptops, smartphones, and tablets connect to the WLAN using network interface controllers.
One of the primary advantages of WLAN is its flexibility. Unlike traditional LAN setups, WLAN does not require extensive wiring or physical connections between devices. This makes it ideal for situations where running cables is impractical or impossible. Moreover, WLANs can be set up quickly and easily, making it a popular choice for home users and small businesses.
WLAN offers several benefits over traditional LAN setups. One of the primary advantages is increased mobility. Since WLANs do not rely on physical connections between devices, users can move around freely within the network area without worrying about cables. This makes WLAN ideal for users who need to move around a lot, such as students, business travelers, and employees who work from home.
Another key advantage of WLAN is its scalability. Since WLAN is a wireless technology, it can be easily expanded or contracted as needed. This makes it ideal for businesses that require flexible networking solutions, such as companies with fluctuating staffing levels or those that need to accommodate multiple devices.
In conclusion, Wireless Local Area Networking is a modern technology that provides wireless access to the internet or other network resources within a specific area. It uses radio waves to transmit data over short distances, and it is highly flexible and scalable. WLAN offers several advantages over traditional LAN setups, including increased mobility and scalability, making it an ideal choice for home users, small businesses, and enterprises alike.





