What Is Volumetric Capture and How Does It Work?
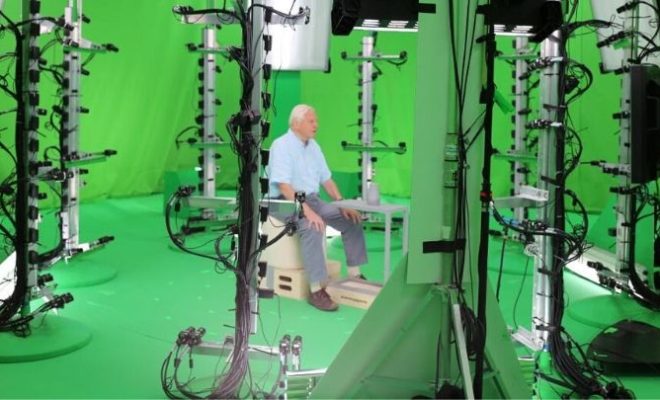

Volumetric capture refers to the process of creating a three-dimensional (3D) digital representation of a real-world object or space. Unlike traditional 3D modeling techniques that require manual modelling, volumetric capture automates the process by using advanced sensors and cameras to record and capture the physical space.
In simpler terms, volumetric capture is a technology that allows filmmakers, game developers, and other creatives to capture real-life objects and environments in 3D, which can then be used in movies, video games, virtual reality (VR), and augmented reality (AR) experiences.
To understand how volumetric capture works, let’s take a look at the three basic components of the process:
1. Sensors and cameras: Volumetric capture uses a combination of sensors and cameras to capture the real-world environment in 3D. These sensors can be laser scanners, depth-sensing cameras, or photogrammetry cameras that capture multiple images in a short period of time. These sensors and cameras are strategically placed around the target space to capture all angles.
2. Processing software: Once the sensors and cameras capture the physical space, the captured data is fed into powerful software that processes the information and creates a digital replica of the real-world object or space. The software uses intricate algorithms to determine the position, orientation, and distance of each sensor to accurately recreate the space.
3. Output: The final output of the volumetric capture process is a highly detailed 3D model that reflects the physical reality of the object or space. The model can be exported in various formats, such as computer-aided design (CAD) files, 3D models, or point clouds. This data can be used to create immersive experiences, such as VR, AR, and movies.
Now that we understand how volumetric capture works, let’s explore its applications.
Volumetric capture is used in a variety of industries, from gaming to film production. For example, game developers use this technology to create highly detailed 3D models of characters, environments, and objects that are used in video games. Movie producers use volumetric capture to create realistic special effects, such as explosions, fire, and other visual effects.
Volumetric capture is also used in medical imaging, architecture, and heritage preservation. For example, medical professionals use this technology to create 3D models of patient scans, allowing for precise surgical planning and diagnosis. Architects use this technology to create 3D representations of buildings and spaces, allowing them to see how constructions will look and function before they are built. Heritage sites use volumetric capture to preserve cultural sites and artifacts for future generations.
In conclusion, volumetric capture is a powerful technology that allows for the creation of highly detailed 3D models of real-world objects and environments. Its various applications make it a valuable tool for creatives, professionals, and researchers alike. As technology continues to evolve, volumetric capture is sure to become an even more critical tool for innovation and exploration.