What is Solid-State Storage (SSS)?
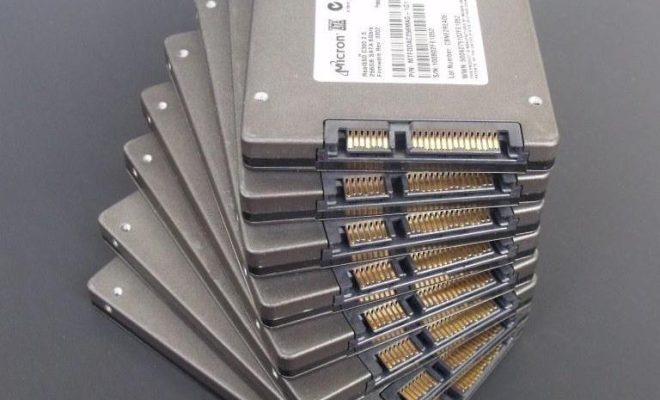

Solid-State Storage (SSS) is a type of storage technology used to store data in a computer or other electronic device. Unlike traditional hard drives, which use spinning disks to read and write data, solid-state storage uses microchips to store and retrieve data.
The most significant advantage of solid-state storage over traditional hard drives is speed. Solid-state drives (SSDs) can access data much faster than hard drives because they have no moving parts. This means that data can be retrieved and stored almost instantly, which makes solid-state storage ideal for use in applications that require fast access times, such as gaming, video editing, and other high-performance computing tasks.
Another advantage of solid-state storage is its durability. Because there are no moving parts in an SSD, there is no risk of mechanical failure due to shocks or vibrations. This makes solid-state storage a popular choice for use in laptops and other mobile devices where there is a higher risk of physical damage.
Solid-state storage is also more energy-efficient than traditional hard drives. Because there is no need for a motor to spin a disk, solid-state storage consumes less power than traditional hard drives. This makes it an ideal choice for use in devices such as smartphones and tablets, where battery life is a primary concern.
There are several different types of solid-state storage, including single-level cell (SLC), multi-level cell (MLC), and triple-level cell (TLC) technologies. SLC is the most expensive but offers the best performance and durability, while TLC is the least expensive but offers the lowest performance and durability.
Some potential drawbacks to solid-state storage include cost and capacity limitations. Solid-state storage can be more expensive than traditional hard drives, especially when high capacities are required. Additionally, the maximum capacity of a solid-state drive is typically lower than that of a traditional hard drive, which may make it less suitable for use in applications that require large amounts of storage.