What is Server Mirroring?
Server mirroring, also known as mirror server or failover, is a popular method of data backup that helps ensure high availability of data and applications in the event of a system failure. It is a process of replicating data from one server to another, creating an exact copy of the original data.
In the traditional backup system, data is typically backed up to an external storage device, such as a tape, disk, or cloud. In case of a system failure, the data can be restored from the backup device, but this process can often take longer, resulting in downtime that can lead to financial losses.
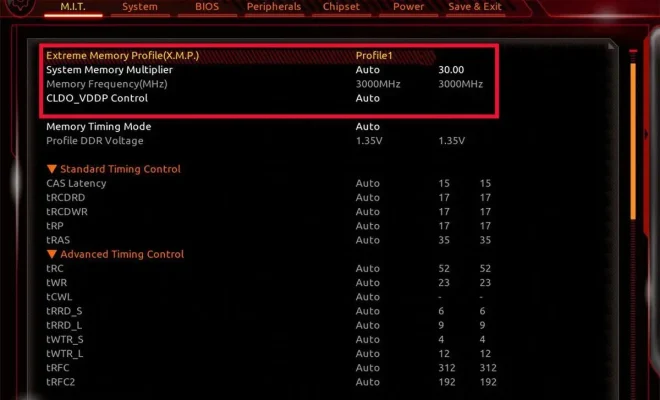
Server mirroring offers a quicker solution to system failures. It uses a secondary server that mirrors the data of the primary server in real-time. So if the primary server goes down or faces any issues, the secondary server can instantly take over, and users can continue to work without any system downtime.
Technically, the process of server mirroring uses a software or hardware-based technology that automatically synchronizes data between two servers. The primary server is designated as the source server, and the secondary server is set as the destination server. Every change made on the primary server is automatically sent to a mirror server, so the data remains in sync.
There are two types of server mirroring, synchronous and asynchronous. In synchronous mirroring, data is written simultaneously to both source and destination servers, ensuring that both servers have the same data at any given time. Asynchronous mirroring, on the other hand, sends data to the mirror server with a delay of a few seconds, ensuring that the mirror server can catch up.
Server mirroring has several benefits. It helps ensure high availability of critical applications and data, minimizes the risk of data loss with near-instant failover, enables quick recovery times, and can provide protection against disasters such as hardware failures, data corruption, and data breaches.