What is Network Topology?

Network topology refers to the physical or logical arrangement of a network. It defines how a network is set up and how data is transmitted between different nodes or devices within the network.
Network topology is a critical aspect of any network infrastructure as it facilitates communication between various devices and ensures that data is exchanged seamlessly.
While there are various network topologies available, the primary ones include:
1. Bus Topology:
In the bus topology, all devices connect to a central cable called a bus. Data is transmitted over this cable, and each device can access the data simultaneously.
2. Ring Topology:
In the ring topology, each device is connected to two other devices, forming a ring-like structure. Data is transmitted in one direction, and each device copies the data before it passes on to the next device in the ring.
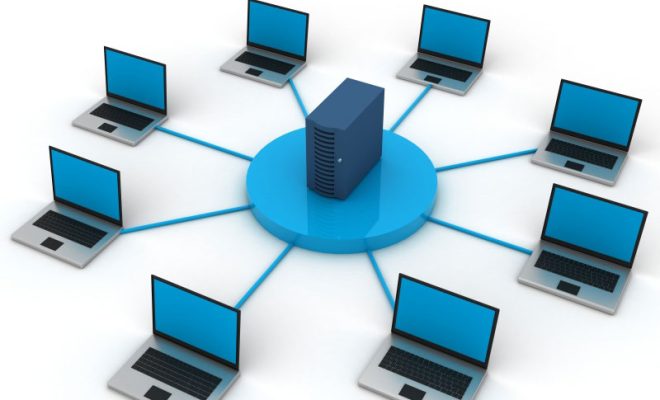
3. Star Topology:
In the star topology, all devices are connected to a central hub or switch. Data is transmitted from the devices to the hub and then transmitted to the destination device.
4. Mesh Topology:
In the mesh topology, all devices are connected to each other. Data is transmitted from one device to another and then onwards to the final destination.
5. Hybrid Topology:
In the hybrid topology, two or more topologies are combined. For instance, a network may have a ring topology in one area and a star topology in another area.
The network topology determines the network’s scalability, availability, reliability, and security. For example, a bus topology may not be suitable for a large network as it can clog up and affect the network’s performance. On the other hand, a mesh topology is more scalable and offers more resilience.
In conclusion, selecting the right network topology is critical to the success of any network. Factors such as the size of the network, the sensitivity of the data being transmitted, and the applications running on the network must be taken into account when selecting a network topology.