What Is an IP Address Conflict?
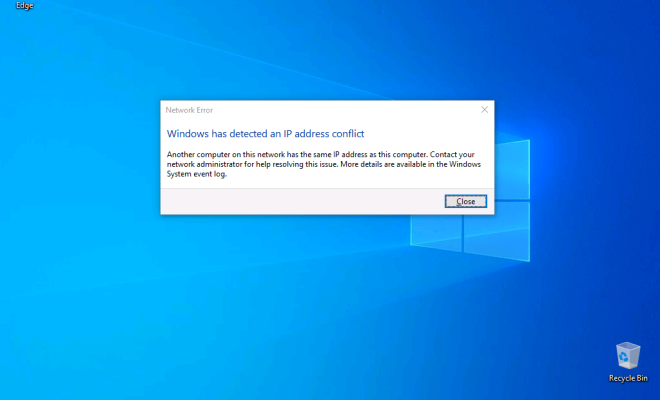
An IP address conflict occurs when two devices on the same network have been assigned the same IP address. This can create issues with communication and connectivity between devices, causing network connectivity problems.
IP addresses are unique identifiers used by devices to communicate with each other on a network. When a device is connected to a network, it is assigned an IP address by the network’s DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) server. This IP address is usually temporary and can be changed frequently.
IP address conflicts occur when two devices on the same network are assigned the same IP address. This can happen for several reasons, including:
1. Static IP addresses
When a device is assigned a static IP address instead of an automatically assigned IP address. This can create conflicts if another device is assigned the same static IP address.
2. DHCP server failure
When the network’s DHCP server fails to assign a unique IP address to a device, it can create a conflict with another device on the network.
3. Network changes
Adding new devices or changing network configurations can also create IP address conflicts if the DHCP server does not update the IP addresses of existing devices on the network.
When an IP address conflict occurs, devices on the network may experience connectivity issues, such as slow internet speeds, intermittent connectivity, or complete loss of network connection.
Resolving an IP address conflict usually requires troubleshooting the network configuration and resolving the cause of the conflict. This can involve releasing and renewing IP addresses, checking the DHCP server configuration, checking for duplicate IP addresses, and resetting network configurations.
To prevent IP address conflicts, it is important to follow proper network configuration practices, such as using dynamic IP addresses instead of static addresses, keeping DHCP servers up to date, and regularly checking network configurations for any changes.
In conclusion, IP address conflicts can cause significant connectivity issues on a network, but they can be resolved by carefully troubleshooting the network configuration and taking steps to prevent future conflicts. By practicing good network configuration, organizations can avoid issues with IP address conflicts and ensure smooth network communication.






