What is a Storage Device?
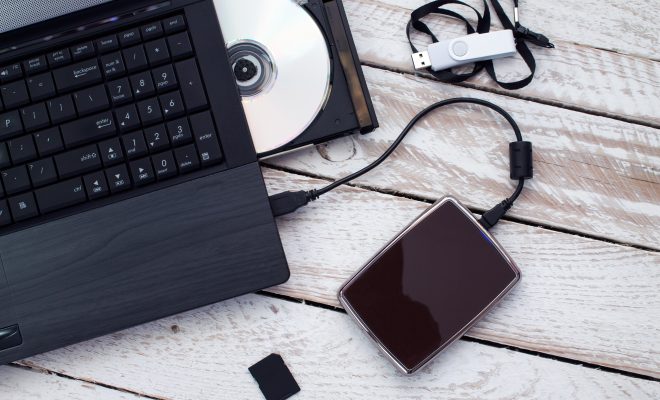

A storage device is any piece of hardware that is used to save and retrieve data that can be later accessed by a computer system. From a technical perspective, a storage device can be either electronic, magnetic, optical, or even mechanical in form. These devices are used to hold and store data, such as documents, pictures, videos, and music.
There are many different types of storage devices that are commonly used today, each with their own unique characteristics, capabilities, and limitations. Some of the most popular storage devices include solid-state drives, hard disk drives, USB flash drives, memory cards, optical disks, and tape drives.
Solid-state drives (SSDs) are a type of electronic storage device that use NAND-based flash memory to store data. SSDs are fast, efficient, and reliable, making them a popular choice for high-performance computing applications.
Hard disk drives (HDDs) are mechanical storage devices that use spinning disks to store data. HDDs are slower than SSDs but offer much larger capacity and are often used in desktop computers, laptops, and servers.
USB flash drives are small, portable storage devices that are very popular for carrying data between devices. Memory cards are similar to USB flash drives but are often used in cameras, phones, and other handheld devices that require removable storage.
Optical disks, such as CDs, DVDs, and Blu-Ray discs, use lasers to read and write data onto a reflective surface. These disks offer large capacity and durability but are relatively slow compared to other storage devices.
Tape drives are a type of magnetic storage device that have been used for many years in large-scale data centers. They offer very high capacity but are relatively slow and are now being replaced by more modern storage technologies.
All of these storage devices are essential components in modern computing systems, enabling users to store and retrieve data easily and efficiently. As technology continues to develop, new storage devices will continue to emerge, each offering their own unique features and capabilities.