What is a Secondary Storage Device?
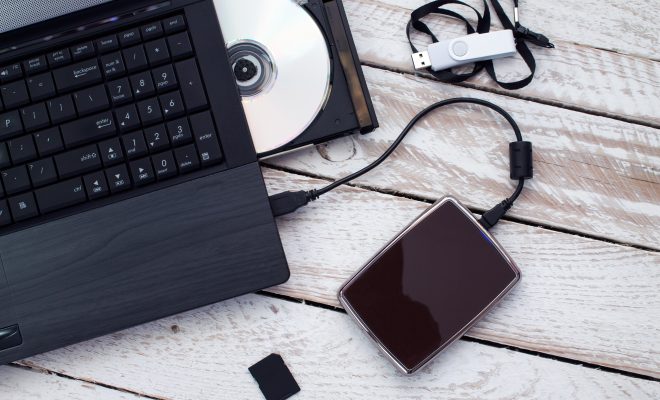

In computing, a secondary storage device refers to any device used for storing data outside of the computer’s primary memory. These devices provide a means for storing large amounts of data for extended periods of time, safeguarding against data loss and providing an additional layer of backup protection.
Secondary storage devices can take many forms, with the most common being hard disk drives, solid-state drives, magnetic tape, and optical disks. Each of these devices has its unique features, advantages and disadvantages.
Hard disk drives (HDD), being the most commonly used secondary storage device, have been an essential component of computer systems for decades. Many laptops, desktops, and servers use hard drives to store data. Hard drives are relatively cheap, have large storage capacities and can retrieve files quickly.
On the other hand, solid-state drives are similar to hard drives, but instead use flash memory to store data. Solid-state drives boast the fastest read and write speeds, can last longer, and are more resistant to physical damage than hard drives.
Magnetic tape, an older technology, is still used today for long-term data backup storage. These tapes are less expensive than hard drives or solid-state drives, but have slower data transfer rates.
Optical disks, such as CDs and DVDs, have limited storage capacity but are still used to store data for backup purposes. They are relatively cheap and portable, making them ideal for sending large files or storing data offsite.
The use of secondary storage devices is vital for businesses, organizations, and individuals who wish to protect their data and ensure its longevity. Without a secondary storage device, they risk data loss, corruption, or theft. Additionally, for businesses and organizations, secondary storage devices are instrumental in disaster recovery plans to ensure business continuity in the event of a disaster or system failure.
In conclusion, secondary storage devices are essential components in computer systems, providing additional storage capacity and backup protection for critical data. With the variety of options available, including hard drives, solid-state drives, magnetic tapes, and optical disks, organizations and individuals have several options to choose from when selecting a secondary storage device that best meets their needs.