The Different Types of Computer Memory & Storage Explained
Computer memory and storage play a crucial role in the overall performance of any computer system. They are responsible for storing and organizing data, program files, and even the operating system. However, not all memory and storage devices are created equal, and each one has a specific function and purpose. In this article, we will explore the different types of computer memory and storage and explain their respective roles in computing.
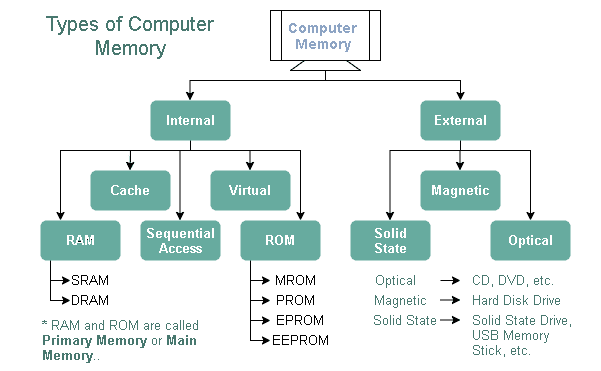
Random Access Memory (RAM)
RAM, or Random Access Memory, is a type of computer memory that stores program instructions and data temporarily. It’s a volatile memory, which means that it loses its contents when the computer is turned off. RAM’s primary function is to hold the temporary data that the CPU needs to access quickly while it’s running programs. The more RAM a computer has, the more programs it can run simultaneously.
There are two types of RAM – Dynamic RAM (DRAM) and Static RAM (SRAM). DRAM is the most common type of RAM and is used in most computers today. It is affordable, fast, and has high capacity. On the other hand, SRAM is faster and more expensive than DRAM, but its capacity is limited.
Read-Only Memory (ROM)
Read-Only Memory, or ROM, is a type of computer memory that permanently stores data and instructions. ROM is non-volatile, which means that it retains its contents even when the computer is turned off. The data stored in ROM includes the basic input/output system (BIOS), firmware, and other critical software that the computer needs to start up and function.
ROM cannot be rewritten, and its content is set at the time of manufacturing. Therefore, updates and changes cannot be made on a ROM chip. However, some modern computers use a type of ROM called EEPROM (Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory), which can be reprogrammed with a special tool or software.
Hard Disk Drive (HDD)
A Hard Disk Drive, or HDD, is a type of magnetic storage device that stores data on spinning disks. An HDD is the most common type of storage device found in desktop and laptop computers. It provides high-capacity storage at an affordable price, making it ideal for storing files, programs, and the operating system.
However, an HDD is relatively slow compared to other types of storage, such as Solid State Drives (SSDs). This is because its spinning disks must physically move to access each bit of data, which slows down data access times. Despite this, the HDD remains a popular choice due to its affordability and high storage capacity.
Solid State Drive (SSD)
A Solid State Drive, or SSD, is a type of storage device that doesn’t use spinning disks. Instead, it stores data on flash memory chips, which are faster and more reliable than traditional spinning disks. SSDs are significantly faster than HDDs, and they are more durable and resistant to shocks, making them an ideal choice for laptops or portable devices.
However, SSDs are more expensive than HDDs, and they typically have lower storage capacity. This means that they may not be the best choice for storing large files or for users who require a lot of storage space.
Conclusion
In conclusion, computer memory and storage play a significant role in the performance of any computer system. Understanding the different types of memory and storage can help you choose the right components for your computer to meet your needs. Whether you need high-capacity storage or fast data access times, there is a memory or storage device available to suit your specific requirements.