SIM Card

The SIM card, an acronym for Subscriber Identity Module, is an essential component in mobile devices, playing a pivotal role in connecting users to their mobile network providers. This compact chip enables secure storage of personal information and telecommunication services, such as phone numbers, and text messages. In this article, we will delve into the world of SIM cards, discussing their history, types, and how they work.
History of SIM Cards
SIM cards were first introduced in 1991 by Munich smart card maker Giesecke & Devrient. Initially designed for GSM (Global System for Mobile Communication) networks, they later evolved as network technology advanced.
From the early credit card-sized format to the micro and nano-sized versions we use today, the SIM card’s miniaturization mirrors advancements in mobile technology.
Types of SIM Cards
There are several types of SIM cards on the market today:
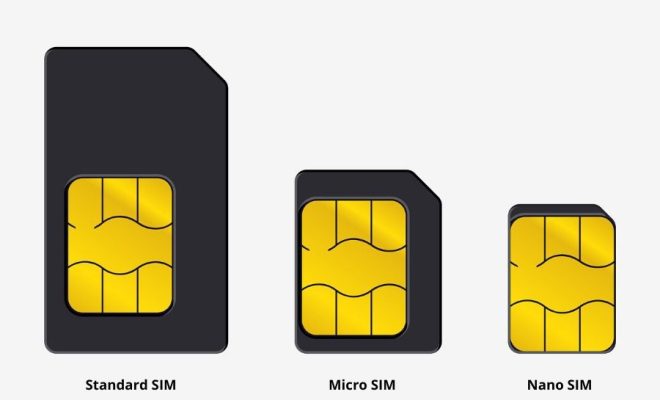
1. Standard SIM: The first type of SIM card that was introduced; it is about the size of a credit card (85.60 mm × 53.98 mm × 0.76 mm) but now phased out by most carriers.
2. Mini-SIM: Measuring 25 mm x 15 mm x 0.76 mm, this smaller version succeeded the standard SIM and is still used in some older mobile phones.
3. Micro-SIM: At 15 mm x 12 mm x 0.76 mm dimensions, the micro-SIM is found in many modern smartphones.
4. Nano-SIM: The smallest and currently popular type, with dimensions of 12.3 mm x 8.8 mm x 0.67 mm.
How SIM Cards Work
SIM cards play a crucial role in maintaining communications between a user’s device and their respective network provider.
– IMEI (International Mobile Equipment Identity) Number – A unique identifier for every mobile device, which ensures the proper device is being used on a network.
– IMSI (International Mobile Subscriber Identity) Number – A unique 15-digit number identifying the user on a network, allowing calls, messages, and data usage to be accurately billed.
When a user inserts a SIM card into their device, the IMSI and additional encryption keys are read by the mobile network. Once verified, the device connects to the network and maintains communication while ensuring secure connections.
Final Thoughts
SIM cards are indispensable components for modern mobile devices. They not only store valuable personal information but also facilitate secure communication between mobile devices and network providers. As new digital technologies emerge – such as eSIMs (embedded SIM cards) – we can expect further advancements in this critical aspect of mobile communication.