What Is Intermodulation Distortion (IMD)?
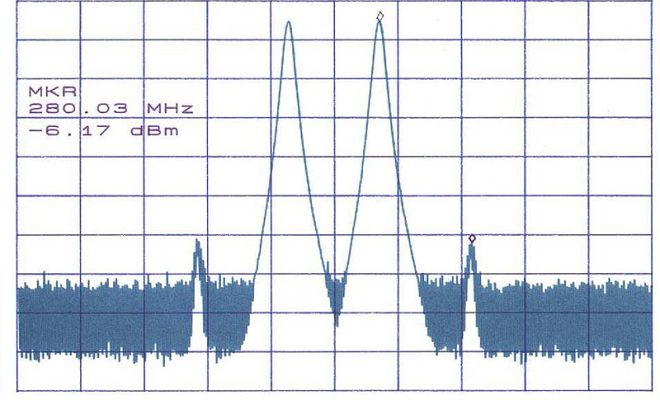
Intermodulation distortion, or IMD, is a type of distortion that occurs in electronic systems. It is caused by the interaction of two or more signals that are being processed simultaneously and can affect the performance of audio, radio, and other communication systems. In this article, we will discuss what IMD is, how it is caused and how to mitigate it.
What is Intermodulation Distortion?
Intermodulation Distortion occurs when two or more signals are mixed together and create new frequencies that are not present in the original signals. This can happen at any point in the signal-chain, from input stages to the output stages. The result is that the original signals become distorted or corrupted by the new signals, and this can cause interference and degradation of the original signals.
The distortion products that are created by IMD are typically a combination of original frequencies and their harmonics, which are frequencies that are multiples of the original frequencies. These harmonics can sometimes fall into the same frequency range as the original signals or even outside of it, and this can result in crosstalk and signal interference.
What Causes Intermodulation Distortion?
Intermodulation distortion is caused by nonlinearities in electronic circuits. A nonlinear circuit is one that doesn’t follow a linear relationship between input and output. When two or more signals are mixed together in a nonlinear circuit, it can cause the circuit to produce new frequency components that were not in the original signals.
Some of the common sources of nonlinearities in electronic circuits that can cause IMD include:
– Amplifiers
– Mixers
– Filters
– Oscillators
– Transmission lines
– Passive components such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors.
How to Mitigate Intermodulation Distortion?
Intermodulation distortion can be mitigated by using techniques such as frequency planning, filtering, and equalization. The following are some of the ways to reduce or prevent IMD:
1. Frequency Planning:
By properly planning the frequency ranges used by different signals in a system, the chance of intermodulation distortion can be significantly reduced. This can be achieved by selecting frequencies that are far apart from each other and using appropriate bandwidths for each signal.
2. Filtering:
By using filters to remove unwanted frequencies that might cause IMD before they enter the circuit, it can help reduce the overall distortion in the system.
3. Equalization:
By equalizing the signals that are being mixed in terms of their level and phase, it can help reduce the potential for intermodulation distortion.
4. Temperature control:
Since temperature can also cause nonlinearities in electronic components, controlling the temperature of the system can also help reduce the risk of IMD.
Conclusion
Intermodulation distortion is a type of distortion that can occur in electronic signals when multiple signals are processed together. To prevent or reduce the effects of IMD, techniques such as frequency planning, filtering, and equalization, and temperature control can be used. By understanding what causes IMD and taking measures to prevent it, electronic systems can function more effectively and deliver high-quality signals.