What Is a DICOM File?
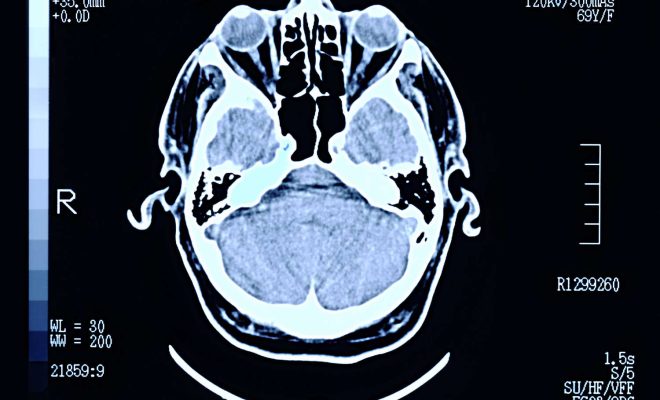
DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine) is the standard format for medical imaging files. The DICOM file format is used by healthcare professionals to transfer medical images such as X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans between healthcare systems, medical imaging software, and PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication System). Imaging data stored in DICOM files can not only contain images, but also patient information, physician annotations, and other metadata.
The DICOM file format is essential in the medical field for two main reasons. Firstly, it provides a way for medical professionals to share medical images and patient information electronically, which can significantly improve patient care. Secondly, it allows for easier analysis and interpretation of medical images, since DICOM files are compatible with various medical imaging software.
DICOM files can store a wide range of medical images, such as mammograms, ultrasounds, and PET scans. The images in DICOM files are made up of pixels (picture elements) that represent different shades of grey, with the brightness of each pixel corresponding to the intensity of the x-ray or other type of radiation used to create the image. While DICOM files consist mainly of image data, they also include metadata such as patient details, imaging equipment parameters, and the type of imaging modality used.
The DICOM file format has many advantages over other image file formats, such as JPEG or PNG. DICOM files are optimized for medical imaging – they are designed to include all the necessary information required to interpret the image accurately. This information is stored in the metadata of the file, which is not present in other image file formats.
DICOM files can be viewed using specialized software, such as medical image viewers or PACS systems. This software allows medical professionals to view multiple images from different modalities, such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs, side by side, which can be useful for diagnostic purposes. The metadata of a DICOM file can also provide additional information such as measurements or annotations made by physicians, further improving the accuracy and usefulness of the image.
In conclusion, DICOM files are the standard file format used for storing and exchanging medical imaging data. They allow for the sharing and interpretation of medical images between healthcare providers, and contain important metadata that provides context and additional information about the medical images. The DICOM file format has become an essential tool in modern medicine, and continues to play a crucial role in the diagnosis and treatment of patients.