What Is a Crossover Cable and How Does It Work?
A crossover cable is a type of Ethernet cable that is used to connect two similar devices directly to each other, such as two computers or two switches. Unlike a straight-through cable, which connects different devices, a crossover cable’s wiring is specifically designed to allow for direct communication between devices of the same type.
The usual setup in most networks involves connecting a computer to a switch or router through a straight-through cable. A straight-through cable has a specific pin layout, where the transmitting and receiving lines are connected from end to end. When two similar devices like two computers or two switches are connected, an attempt to use a straight-through cable will fail to provide any communication between the two.
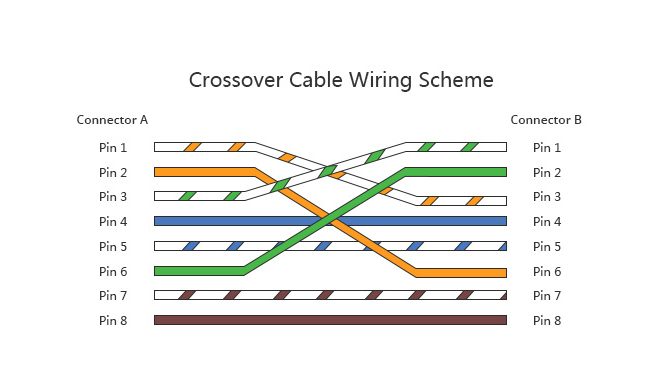
This is where the crossover cable becomes useful. The pin configuration of a crossover cable is different from that of a straight-through cable. In a crossover cable, some of the transmitting lines are swapped with the corresponding receiving lines. This means that when two similar devices are connected using a crossover cable, each device’s transmitter is connected directly to the other device’s receiver, allowing for two-way communication.
A typical Ethernet cable has four pairs of wires, which we refer to as 1, 2, 3, and 6. In a crossover cable, wires 1 and 2 are swapped with wires 3 and 6. So, when a computer sends data through wire 1, it goes directly into the other computer’s receiving wire, 3. This allows the two computers to communicate with each other directly.
Apart from connecting two computers directly, crossover cables can also be used to connect two switches or hubs together. The use of a switch, in this case, is to create a larger network by connecting multiple devices to the same network.