What Is a CCD (Charge-Coupled Device) and How Is It Used?
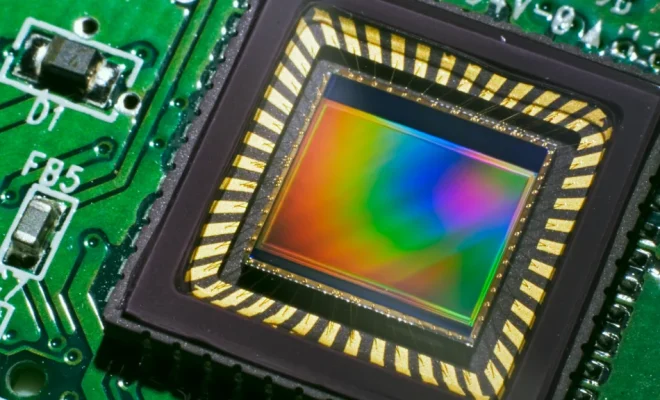
CCD, or Charge-Coupled Device, is a device that is widely used in fields such as digital photography, video recording, and scientific research. It is a technology that has revolutionized the way photos and videos are captured and processed. This article will explain what a CCD is and how it is used.
What is a CCD?
A CCD is a type of image sensor that converts light into an electrical charge. It was invented by George E. Smith and Willard Boyle in 1969 and has since been used in various applications, including astronomy, digital photography, and video recording. CCDs consist of an array of light-sensitive diodes that convert photons (light particles) into electrons (electrical charges).
How does a CCD work?
When light enters a CCD, it strikes the light-sensitive diodes (also known as pixels) and generates electrons. These electrons are then transferred from one pixel to the next using a process called charge-coupling, hence the name Charge-Coupled Device. The electrons are then read out by an output amplifier, which converts the electrical charge into a digital signal that can be processed by a computer.
What are the benefits of using CCDs?
CCDs offer several benefits over other types of image sensors, such as CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) sensors. One of the main advantages is their ability to produce high-quality images with minimal noise. CCDs are also very sensitive to light, which makes them ideal for low-light photography and scientific applications.
How are CCDs used in digital photography?
In digital photography, CCDs are used to capture light and create digital images. When you take a photo, the light enters the camera lens and hits the CCD sensor, creating an electrical charge that is stored as data. This data is then processed by the camera’s internal processor to create a digital image.
CCDs are also used in video recording, where they enable high-quality video with low noise. They are often used in security cameras, surveillance systems, and broadcast television.
How are CCDs used in scientific research?
CCDs play a vital role in scientific research, especially in astronomy. They are used to capture images of distant objects such as planets, stars, and galaxies. The images captured by CCDs are used to study the properties of these objects, such as their size, temperature, and composition.
In conclusion, CCDs are a powerful technology that has revolutionized the way images and videos are captured and processed. They offer high-quality images with minimal noise, making them ideal for applications such as digital photography, video recording, and scientific research.






