What Is a Capacitor and What Is It Used For?
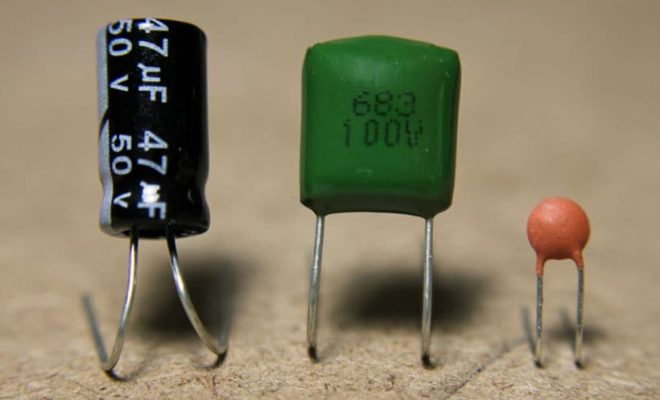
A capacitor is an electronic device used to store electrical energy. It consists of two conducting plates separated by an insulating material called a dielectric. When an electric charge is applied to the plates, it is stored in the electric field between them.
Capacitors are used in a variety of applications where energy storage, energy discharge, or filtering of signals is required. One of the most common uses of capacitors is as a filter in AC circuits. In these circuits, a capacitor is used to smooth out fluctuations in voltage or current by storing energy during peaks and releasing it during dips.
Capacitors are also used in electronic circuits to block DC voltage while allowing AC signals to pass through. This type of capacitor is called a coupling capacitor, and it is used to separate the AC component of an electronic signal from the DC component.
Another common use of capacitors is in power supplies. Here, capacitors are used to store electrical energy and quickly release it when needed. This helps to ensure a stable and consistent supply of power to electronic devices.
Capacitors are also used in timing circuits, where they are used to control the timing of electronic signals. In these circuits, a capacitor is charged to a certain voltage and then discharged through a resistor. The time it takes for the capacitor to discharge to a certain level is determined by the capacitance of the capacitor and the resistance of the resistor.
In addition to these applications, capacitors are also used in electric motors, fluorescent lighting, and audio equipment. In motors, capacitors are used to start the motor by providing a brief burst of energy. In fluorescent lighting, capacitors are used to regulate the flow of current through the lamp. In audio equipment, capacitors are used to filter out unwanted noise and feedback.






