Satellite Internet Explained
Introduction:
The rapid advancements in technology have enabled many to stay connected at all times. One such innovation is satellite internet, which allows users to access the internet from virtually anywhere on the globe. This article will delve into the workings of satellite internet and discuss its various features.
How Satellite Internet Works:
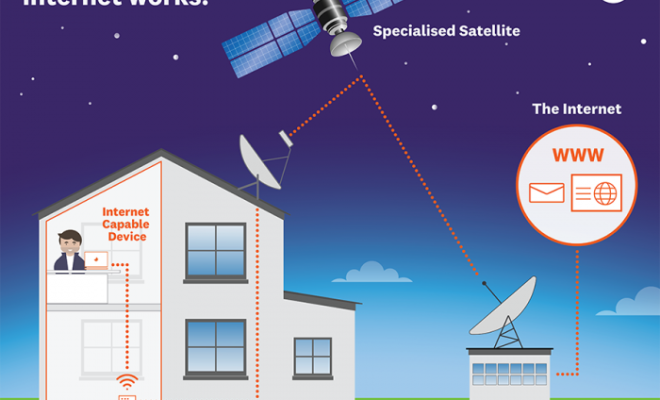
Satellite internet operates through a network of satellites stationed in space. To access this service, you need a satellite dish and a modem. When you request information, such as loading a webpage or streaming a video, the signal travels from your satellite dish to the modem and then up to an orbiting satellite. The satellite, in turn, sends the signal to a ground station called Network Operations Center (NOC), which processes your request and sends back the information through the same path.
Advantages of Satellite Internet:
1. Coverage: Satellite internet provides coverage in remote areas where traditional terrestrial broadband services may be unavailable or unreliable.
2. Quick installation: Setting up a satellite system is typically faster and less intrusive than other methods, such as running cables through trenches.
3. Reliable service: Satellite connections are less likely to be affected by severe weather conditions or natural disasters compared to terrestrial networks.
Disadvantages of Satellite Internet:
1. Latency: The time it takes for data signals to travel between satellites, NOC, and back can cause delays (latency) in browsing and online gaming experiences.
2. Costs: Equipment and subscription fees for satellite internet tend to be higher than traditional broadband alternatives.
3. Line-of-sight issues: Obstructions like tall trees or buildings can block signals between your dish antenna and the orbiting satellites.
The Future of Satellite Internet:
Technological advancements are working towards overcoming existing limitations associated
with satellite internet. Companies like SpaceX with their Starlink Project, OneWeb, and Amazon’s Project Kuiper aim to create Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellite constellations. These LEO satellites, situated closer to Earth, promise to reduce latency and improve overall performance significantly.
Conclusion:
While satellite internet may have its limitations, it is an essential service that brings high-speed internet access to remote or underserved regions. The ongoing innovations and investments in the field ensure that satellite internet will continue to improve and provide a viable option for users worldwide.





