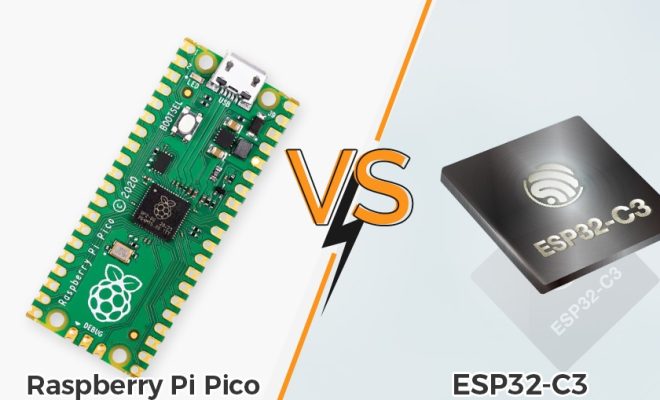
Raspberry Pi Pico vs. ESP32: Which Microcontroller Is Right for You?

With the rise in popularity of the Internet of Things (IoT), microcontrollers have become an essential tool for developers and hobbyists alike. Two of the most popular options in the market right now are the Raspberry Pi Pico and the ESP32. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at both and help you decide which microcontroller is right for you.
Raspberry Pi Pico
The Raspberry Pi Pico is a tiny microcontroller board released by Raspberry Pi in January 2021. It is based on the RP2040 microcontroller chip, which was designed by Raspberry Pi and is built using a 40nm process. The Pico provides 2MB of flash memory, 256KB of RAM, and 26 GPIO pins. It has dual-core processors running at up to 133MHz and supports both MicroPython and C/C++ programming languages.
One of the significant advantages of the Pico is the Open-Source hardware design philosophy that Raspberry Pi has adopted. It means that anyone can design, manufacture, and sell their Pico boards. Additionally, Pico is also very power-efficient, making it ideal for low-power IoT applications.
ESP32
The ESP32 is a low-cost microcontroller board based on the ESP32 module developed by Espressif Systems. It is quite popular due to its AI capabilities, integrated Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth connectivity. The chip comes with 4MB of flash memory and 520KB of RAM, which is enough for most projects. It also has a 240MHz dual-core processor and supports a wide range of programming languages, including MicroPython, C/C++, and JavaScript.
One of the advantages of the ESP32 is its advanced connectivity features. It supports Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and BLE, making it an excellent choice for IoT projects that require extensive connectivity. The board is also compatible with a broad range of sensors and modules, which makes integration and development much more manageable.
Comparison: Raspberry Pi Pico vs. ESP32
Both microcontrollers have their benefits and drawbacks. Here’s how they compare:
Power consumption: Raspberry Pi Pico shines in this aspect. It consumes far less power than the ESP32, making it suitable for battery-powered projects.
Connectivity: While the Raspberry Pi Pico has no built-in Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, the ESP32 board has these features built-in. The board also has a faster processor that handles complex connectivity tasks better.
Programming languages: Both devices support multiple programming languages. However, the Raspberry Pi Pico has better MicroPython support, while the ESP32 has an edge in other programming languages.
Price: The Raspberry Pi Pico is cheaper than the ESP32, though the latter board has many more features.
Which one to choose?
Both microcontrollers are excellent choices, but your selection depends on the kind of projects you want to work on. If you’re interested in low-power projects that don’t require connectivity, then the Raspberry Pi Pico is a perfect fit. On the other hand, if you need advanced connectivity features, the ESP32 offers a far more comprehensive range of capabilities. The price difference between the two boards is negligible, so your choice may ultimately rest on the features you require.
In conclusion, the Raspberry Pi Pico and ESP32 are both powerful microcontrollers that are well-suited for various types of IoT projects. When deciding which one to use, consider the power consumption, connectivity options, available programming languages, and your budget. Whatever your decision, both microcontrollers will provide an engaging learning experience and serve your project needs well.