How to Use the Windows Task Manager
The Windows Task Manager is a powerful tool that can help you manage your computer’s performance and productivity. It allows you to view and close programs, monitor system resources, and troubleshoot issues with your computer. In this article, we will discuss how to use the Windows Task Manager to improve your computer’s performance and productivity.
Opening the Task Manager
The Task Manager can be accessed in several ways. You can press the Ctrl + Shift + Esc keys simultaneously to open it directly. Alternatively, you can right-click on the taskbar and select Task Manager. Another method is to press Ctrl + Alt + Del and select Task Manager from the options available.
Task Manager Tabs
When you open the Task Manager, you will see several tabs- Processes, Performance, App history, Startup, Users, and Details. Below is a brief overview of each tab and its function:
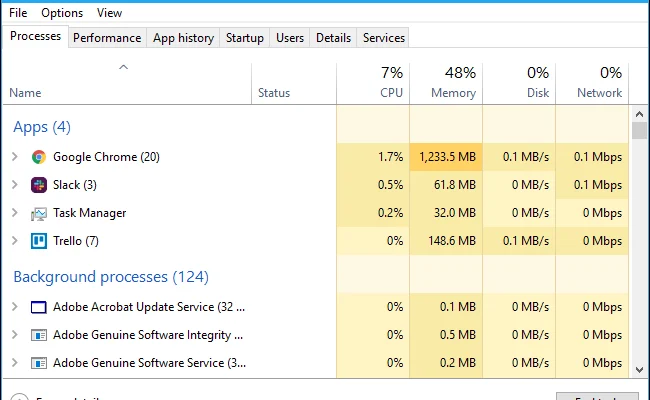
Processes – This tab displays a list of all the running processes on your computer. Each process has a corresponding icon, name, and a description of its impact on your computer’s performance. You can use this tab to monitor the CPU, memory, and disk usage of each process.
Performance – This tab displays a real-time graph of your computer’s CPU, memory, disk, Wi-Fi, and Ethernet activity. You can use this tab to monitor the performance of your computer and identify any bottlenecks.
App history – This tab displays a list of the apps you have used and how resource-intensive they are. You can use this tab to monitor your app usage on your computer.
Startup – This tab displays a list of the programs that start automatically when you turn on your computer. You can use this tab to disable any programs that you no longer want to start automatically.
Users – This tab displays a list of users currently logged into the computer. You can use this tab to disconnect any users who are no longer using the computer.
Details – This tab displays a list of all the running processes similar to the Processes tab. However, this tab displays a more detailed view of each process, including the process ID, CPU time, and priority.
Killing Processes
Sometimes, you may encounter an unresponsive program that is not closing down in the usual way. In such cases, you can use the Task Manager to kill the process. To do this, select the process you wish to end from the “Processes” tab and click on the “End Task” button at the bottom right of the Task Manager window.
Changing Priority of Processes
The Task Manager also allows you to change the priority of processes. This can be useful for giving priority to certain applications over others, usually when running multiple applications concurrently. To do this, select the process whose priority you wish to change from the “Processes” or “Details” tab, right-click on it and select “Set Priority.” Choose the priority level you desire from the available options.





