How Does Lane Centering Work?
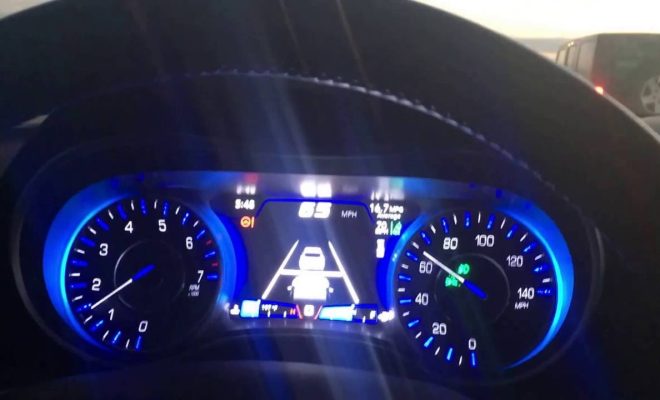

Lane centering is an advanced driver assistance system (ADAS) that is designed to help drivers stay in their lane while driving. It works by using cameras and sensors to detect lane markings and other vehicles on the road, and then automatically adjusting the steering to keep the vehicle centered in its lane.
The technology behind lane centering is complex, but it can be broken down into a few key steps. First, cameras mounted on the front and rear of the vehicle capture images of the road ahead. These images are then analyzed by the vehicle’s computer to detect the presence and position of lane markings.
Once the lane markings have been detected, the system uses sensors to determine the position of the vehicle within its lane. If the vehicle drifts too close to the edge of the lane, the system will automatically apply steering torque to bring the vehicle back to the center of the lane.
Lane centering systems can also detect the presence of other vehicles on the road and adjust the steering accordingly. For example, if the vehicle is following another vehicle too closely, the system may apply steering torque to keep the vehicle centered in its lane and maintain a safe distance from the vehicle in front.
One of the key benefits of lane centering is improved safety. By helping drivers stay in their lane and avoid collisions, lane centering can reduce the risk of accidents and injuries on the road. It can also reduce driver fatigue and improve the overall driving experience.
However, it’s important to note that lane centering is not a fully autonomous driving system. Drivers still need to remain alert and attentive while driving, and should not rely solely on lane centering to navigate the road.
In conclusion, lane centering is an advanced driver assistance system that uses cameras and sensors to keep vehicles centered in their lanes. By improving safety and reducing driver fatigue, lane centering has the potential to make driving a more enjoyable and stress-free experience.