How air-cooled engines work, and why it doesn’t matter any more
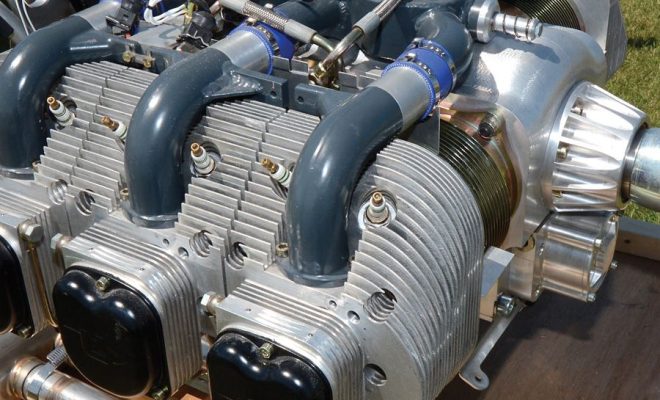

When it comes to engines, technology has advanced at a rapid pace over the years. From traditional air-cooled engines to modern liquid-cooled ones, the scene has evolved immensely. In this article, we delve into how air-cooled engines work, and why they are no longer as relevant in today’s world.
Understanding Air-Cooled Engines
Air-cooled engines employ a simple method to dissipate heat generated by the combustion process, relying on air circulation to cool down the engine components. As the name suggests, these engines do not use any coolant fluid to regulate temperatures. Instead, they have finned cylinders and heads that aid in increasing the surface area for better heat dissipation.
The basic working principle of an air-cooled engine involves drawing ambient air via ducts placed strategically around the engine. As the engine runs, fans powered by the engine push cold air across these fins, cooling them in the process. This continuous cycle keeps the temperature regulated within acceptable limits.
However, air-cooled engines do have some limitations. The most prominent issue is their inability to consistently maintain optimal working temperatures. These engines are vulnerable to overheating in traffic jams or during prolonged idling and may fail to generate sufficient heat during harsh winters.
The Decline of Air-Cooled Engines
There are several key factors contributing to the dwindling relevance of air-cooled engines:
1. Environmental Concerns: Air-cooled engines release more hydrocarbon emissions due to less efficient combustion at less-than-optimal temperatures, which make them less friendly towards the environment.
2. Growing Demand for Fuel Efficiency: Advancements in engine technology have prioritized fuel efficiency and performance enhancement leading to more reliance on liquid-cooled designs that can maintain consistent engine temperatures.
3. Increased Variety of Liquid-Cooled Designs: Modern liquid-cooled systems come with numerous benefits such as improved temperature regulation, better performance, and quieter engine operation, making them the preferred choice for most applications.
Why Air-Cooled Engines Don’t Matter Anymore
In the present-day automotive world dominated by environmental regulations and fuel efficiency requirements, air-cooled engines have simply fallen behind. Liquid-cooled designs have overshadowed them with superior performance, better temperature regulation, and environmentally-friendly emissions.
Air-cooled engines were once popular in automobiles, motorcycles, and even aircraft, but today they are rarely seen apart from specific applications like small generators and lawn equipment. They remain a relic of the past in a world moving towards a future where electric motors and highly efficient internal combustion engines take center stage.
In conclusion, while air-cooled engines have played a significant role in the history of engine technology, their relevance has diminished with time. For automobile enthusiasts and engine experts alike, the rise of liquid-cooled engines reflects a step forward towards more sustainable, high-performance transportation solutions.