Data center cooling systems and technologies and how they work
As data centers are becoming more complex and operate at higher densities, the demand for advanced cooling systems and technologies is growing.There are different types of data center cooling systems, each with their own advantages and disadvantages. Some of the most commonly used ones are:
1. Air cooling systems: Air-cooled systems work by circulating chilled air through the data center. This is done using a variety of methods, including computer room air conditioning (CRAC) units, air handlers, and in-row cooling units.
2. Liquid cooling systems: Liquid cooling systems use water-based coolants to remove heat from the data center. This can be done using either direct or indirect liquid cooling systems.
3. Evaporative cooling systems: Evaporative cooling systems use water to cool the air used in the data center. This is done using methods such as chilled water-cooled air handlers, direct evaporative media, and indirect evaporative cooling.
4. Free cooling systems: Free cooling systems use the outside air to cool the data center during cooler weather conditions. These systems include air-side economizers and water-side economizers.
The most common cooling technologies used in data centers are:
1. Airflow management: This involves managing the flow of air within the data center to ensure uniform cooling and prevent hot spots.
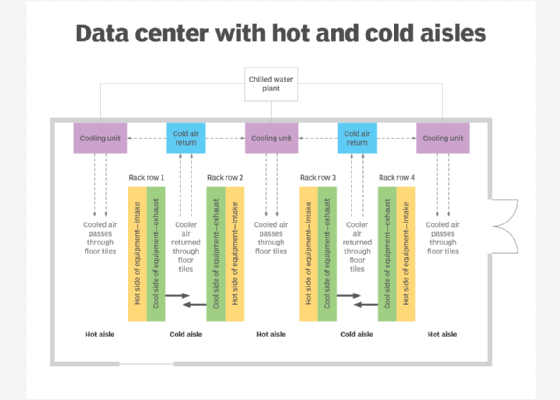
2. Containment: Data center containment involves separating the hot and cold aisles to prevent hot air from mixing with cold air, which can improve cooling efficiency.
3. Heat exchangers: Heat exchangers transfer heat from one fluid to another and are commonly used in liquid cooling systems.
4. Chillers: Chillers are used in liquid cooling systems to cool the water that circulates through the system.
5. Thermal management software: This software monitors and controls the temperature and humidity levels in the data center.
In summary, data center cooling systems and technologies are essential for maintaining the optimal operating conditions of data centers, and there are various options available depending on the data center’s specific needs and requirements.