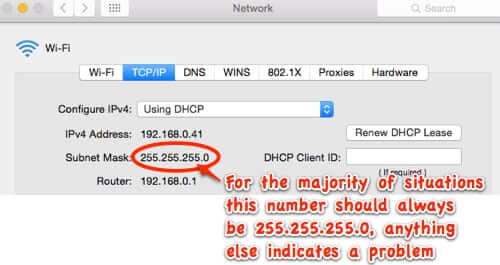
1G, 2G, 3G, 4G, & 5G Explained
In the past few decades, we have seen a rapid evolution of mobile communication technology. From the first generation (1G) to the latest one (5G), each generation of wireless networks has brought new features and capabilities, revolutionizing the way we connect and communicate with each other.
1G
The first generation of wireless networks, 1G, was introduced in the 1980s. 1G allowed for analog voice communication over cell networks, but it had many limitations. The calls could be easily intercepted, and the quality was poor, with lots of static and interference. 1G was also expensive and limited in range, making it impractical for widespread use.
2G
The second generation of wireless networks, 2G, was introduced in the early 1990s. 2G networks marked a significant step forward in mobile communication technology. The main advantage of 2G was digital transmission, which provided better voice quality, improved security, and increased capacity for data transmission.
One of the most significant developments of 2G was the introduction of Short Message Service (SMS), commonly known as texting. SMS allowed for the exchange of short text messages between cell phones. This feature became incredibly popular and is still widely used today.
3G
The third generation of wireless networks, 3G, was introduced in the early 2000s. 3G networks marked a significant leap in terms of data transfer speed and capacity. 3G networks allowed for faster internet browsing and more efficient communication between devices.
One of the most significant developments of 3G was the ability to support multimedia applications such as video calls, video streaming, and web browsing. The speed of 3G networks also allowed for the introduction of mobile gaming and more sophisticated apps.
4G
The fourth generation of wireless networks, 4G, was introduced in the late 2000s. 4G networks marked a significant improvement over the 3G technology, with even faster internet speeds, download and upload speeds up to 100 Mbps, and a broader coverage area.
One of the most significant developments of 4G was the ability to support high-quality video streaming and conferencing, allowing people to communicate visually in real-time. 4G also enabled the development of the Internet of Things (IoT) and the widespread use of wearables technology.
5G
The fifth generation of wireless networks, 5G, is the latest and most advanced mobile communication technology to date. 5G networks provide even faster download and upload speeds, with capacity up to 10Gbps, and latency reduced to as low as 1ms. Higher speeds mean that users have access to high-definition video streaming, fast downloading, and uploading capabilities, and experience augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) gaming, among others.
One of the most significant developments of 5G is its ability to support the Internet of Things (IoT) and enable thousands of connected devices, making it possible to revolutionize smart cities and homes. Other areas that will benefit significantly from 5G are autonomous vehicles, telemedicine, remote education, and electric vehicles, among others.
In conclusion, the evolution of mobile communication technology has gone through several generations, each marking a significant improvement over the previous one. 5G is the most advanced technology to date, with the potential to transform many aspects of our lives. It is expected to bring a new era of innovative technologies and services that will make communication and connectivity easier, faster, and more efficient than ever before.